TAKEAWAY
- Technology fuels transformation: ICT is the catalyst behind innovations that are reshaping how we fight climate change across energy, agriculture, waste, and education.
- Real-time data saves real-world ecosystems: From satellites to sensors, ICT tools give us the intelligence we need to protect forests, track emissions, and predict disasters.
- Digital solutions are accelerating the green economy: Clean tech startups, green data centres, and digital agriculture are making sustainability profitable and scalable.
- ICT bridges the global climate knowledge gap: Online platforms are giving communities access to environmental data, resources, and training.
The future of climate action is digital: As ICT continues to evolve, its potential to drive systemic climate solutions is just beginning.
INTRODUCTION
Can climate change be hacked? Not in the literal sense, but ICT is doing something close to it. From satellites mapping deforestation in real time to AI models predicting floods weeks in advance, technology is fast becoming our most powerful ally for climate change mitigation and adaptation. In a world where every second matters, ICT transforms awareness into action and data into decisions. It’s not just about fighting climate change, it’s about staying one step ahead.
BACKGROUND
Climate change is no longer a distant threat, it’s a present reality. Rising temperatures, shrinking glaciers, and increasingly violent storms are a wake-up call. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) warns that we have until 2030 to cut global emissions in half or risk irreversible damage [1]. But while the threat looms large, a powerful solution lies in our hands in the form of mobile phones, internet access, and digital infrastructure.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) includes everything from software and sensors to broadband and blockchain. According to the Global e-Sustainability Initiative (GeSI), ICT has the potential to reduce global CO₂ emissions by 20% by 2030, even though the sector contributes only about 2-3% of emissions itself [2]. This is a leverage point: When deployed strategically, ICT is not just part of the solution; it amplifies the solution.
Tracking Environmental Challenges, One Pixel at a Time
Technology allows us to see what was once invisible. Satellite systems operated by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (United States) (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and private firms can now detect forest loss, melting ice caps, and methane (CH4) leaks from space. These are critical tools in shaping climate policy and enforcement.
For instance, Global Forest Watch uses satellite data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to monitor forests in real-time, alerting authorities of illegal logging within hours [3]. Meanwhile, the Environmental Insights Explorer by Google helps over 3,000 cities globally track building and transport emissions, helping mayors make data-driven climate decisions [4]. Without ICT, these insights would take months or never come at all.
Smart Agriculture and Green Tech
Agriculture, a major industry which emits greenhouse gases, is undergoing a digital revolution. ICT-powered tools such as precision farming, drone surveillance, and mobile weather forecasting are reducing input waste and increasing yields.
In Kenya, applications like iCow and FarmDrive are helping smallholder farmers adapt to unpredictable weather by offering agricultural tips, weather updates, and access to microloans through mobile-based platforms. In India, sensors connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) are enabling farmers to control irrigation systems via SMS, conserving water while boosting food security. These solutions aren’t just reducing emissions, they are safeguarding our livelihoods and conserving the earth’s natural resources..
In the energy sector, smart grids are optimizing power distribution, cutting losses, and integrating renewables more efficiently. In fact, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), smart energy systems powered by ICT could reduce electricity waste by up to 30% by 2030, aligning with global aligning with global climate goals[5].

Digital Empowerment and Education for Climate
Climate literacy is no longer limited to scientists. Through mobile apps, virtual classrooms, and gamified learning platforms, ICT is making environmental education accessible and engaging.
Applications like Earth Hero and Klima turn climate action into a personal mission, helping users calculate, reduce, and offset their carbon footprints. UN CC: Learn offers free online courses that have educated over 500,000 learners globally on climate resilience, green jobs, and adaptation strategies [6].
In vulnerable communities, ICT is also vital for early disaster warning systems. Text-based alerts on floods, wildfires, and storms have saved thousands of lives in countries like Bangladesh and the Philippines. That’s the power of a single byte in protecting entire populations.
ICT and Circular Economy Innovation
ICT is the backbone of the emerging circular economy, an economic model focused on designing out waste and keeping resources in use. Smart inventory systems, blockchain-powered product tracking, and mobile platforms for sharing or reusing goods are helping consumers and businesses close the loop.
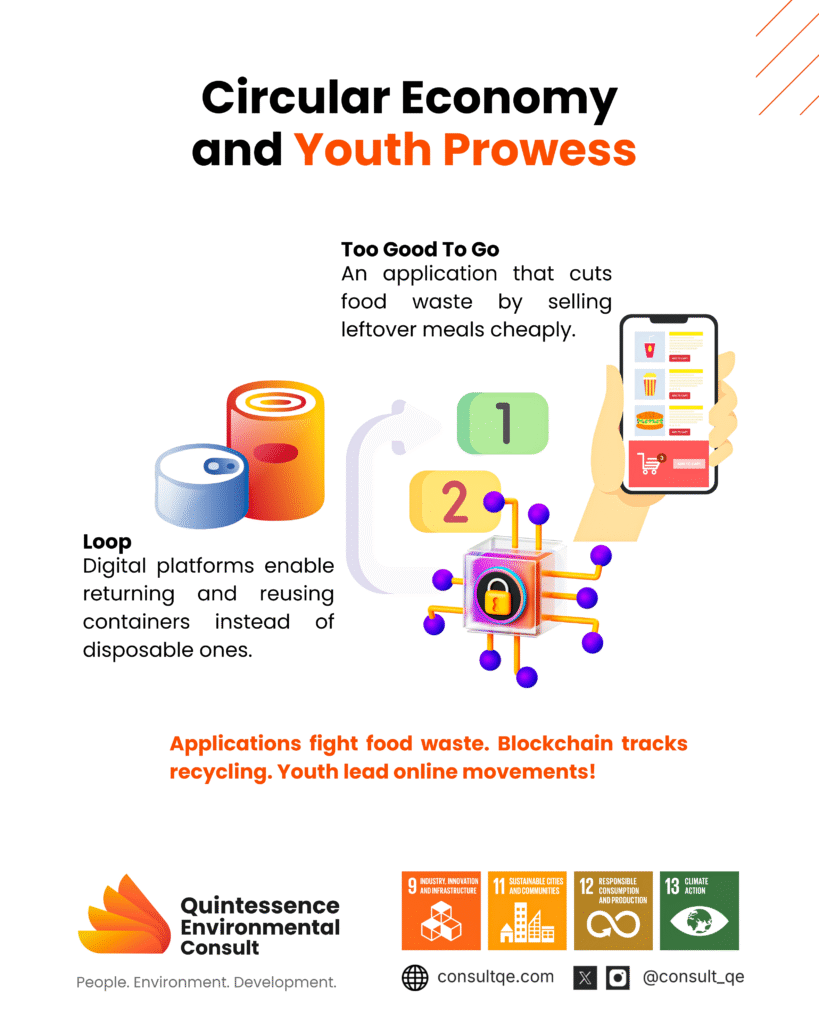
Companies like Too Good To Go, used widely in European countries such as Denmark, France, United Kingdom and Germany, help reduce food waste by using mobile applications that let consumers buy unsold food from restaurants, bakeries, and supermarkets at a discounted price; instead of throwing away perfectly good food at the end of the day. These businesses list it on the application, and users can reserve and pick it up at a lower cost. This way, food that would have gone to waste gets eaten, helping both the environment and people looking for affordable meals.
Startup companies like Loop which launched in the United States, France and the United Kingdom, use digital platforms to manage reusable packaging systems, allowing consumers to return and reuse branded containers instead of relying on single-use packaging. Blockchain, in particular, is enabling transparency in carbon trading, e-waste recycling, and ethical sourcing [7]. These technologies make sustainability measurable, accountable, and profitable.
Youth, Climate, and Digital Advocacy
Young people are leading the digital charge for climate justice. Social media platforms have become megaphones for international movements like Fridays for Future and Stop Ecocide. With nothing more than a smartphone, youth activists from Africa to Asia are organizing protests, sharing climate stories, and pressuring world leaders into action [8].
Additionally, platforms like Youth Climate Lab and Connect4Climate use digital storytelling and mentorship to equip young leaders with the tools to drive change. ICT is lowering barriers, letting even the most marginalized voices influence policy and participate in climate dialogue.
DIGITAL INNOVATION DRIVING CLIMATE SOLUTIONS
ICT’s climate potential goes beyond hardware and software. It’s about systemic change. Digital technologies enable what experts call “dematerialization”: doing more with less. For example, video conferencing replaces air travel, and e-books replace paper. Every kilobyte saved can mean a ton of emissions avoided [2].
However, the ICT sector must also clean its own house. Data centres consume roughly 1% of global electricity, and e-waste from electronics is rising rapidly [5]. But there’s progress, green cloud computing, energy-efficient chips, and carbon-aware coding practices are already reducing tech’s footprint. Major players like Google and Microsoft now run their data centres on 100% renewable energy, setting new standards for green ICT [4].
Looking ahead, technologies like blockchain could create transparent carbon credit markets, while AI could optimize entire cities for energy use. ICT is no longer a support function; it’s a driver of the climate-tech revolution [2].

A CALL TO ACTION
The fight for our planet is no longer just happening in forests, oceans, and factories. It’s happening online, in the cloud, and across networks. It’s time to log in, connect, and act.
- Policy Maker: Invest in digital infrastructure that supports green innovation.
- Business Leader: Adopt ICT tools that track and cut your carbon footprint.
- Young Individual: Utilize mobile devices to advocate and educate on climate action.
- Citizen: Acquire knowledge on climate change and support tech-driven climate action initiatives.
CONCLUSION
From satellite surveillance to sustainable applications, ICT is revolutionizing how we respond to the climate crisis. ICT reduces the climate crisis by enabling real-time environmental monitoring, faster disaster response, scalable education, and data-driven climate strategies. This results in tangible outcomes like reduced emissions, smarter agriculture, and more resilient communities.
Its ability to foster innovation and democratize knowledge makes it one of the most powerful tools in the sustainability toolkit. But this power comes with responsibility.
REFERENCES
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (2023). AR6 Synthesis Report. Retrieved from https://www.ipcc.ch
- Global e-Sustainability Initiative. (2022). SMARTer2030 Report. Retrieved from https://gesi.org/research/smarter2030
- Global Forest Watch. (2024). Real-Time Forest Monitoring. Retrieved from https://www.globalforestwatch.org
- Google Environmental Insights Explorer. (2023). Retrieved from https://insights.sustainability.google
- IEA. (2023). Digitalization and Energy. Retrieved from https://www.iea.org
- UN CC: Learn. (2023). Climate Change Learning Partnership. Retrieved from https://www.uncclearn.org
- World Economic Forum. (2022). Circular Economy and ICT. Retrieved from https://www.weforum.org
- United Nations. (2023). Youth and Climate Action. Retrieved from https://www.un.org/youthenvoy/climate-action

Interesting
Nice piece bro
Other observings systems like GCOS, WIS 2.0, WIGOS and agencies like NOAA, DWD, EUTMETNET are also playing a big role
Impressive. This is quite informative
Nice research, keep posting.
This was a good read
An insightful piece.
Nice research