Reforming Nigeria’s Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining Sector: A Path to Sustainable Livelihoods
deposits of Plateau, Bauchi, and Kano, and the gemstone markets of Kaduna, ASM provides livelihoods where farming or other jobs are limited.
However, this lifeline comes with paradoxes. While ASM reduces rural poverty, supports households, and contributes to mineral output, it is also plagued by informality, unsafe practices, environmental degradation, and lost government revenue. Nigeria faces a crucial choice: continue to allow ASM to operate in the shadows, or reform it into a pillar of sustainable livelihoods and responsible mining.
The sector remains underdeveloped despite Nigeria’s mineral wealth across more than 500 locations in the 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory (FCT). The Nigerian Mining Corporation, once a leading producer, declined after the 1970s indigenization policy, and now contributes 4.38 per cent to the overall GDP in the first quarter of 2025, lower than the 5.47 per cent contribution recorded in the same quarter of 2024, according to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) latest GDP report.[14]
The underperformance stems largely from ASM-related challenges, including informality, weak regulatory oversight, insecurity, smuggling, and under-declaration of exported minerals.
Reimagining Katsina: A Green Growth Vision for All

In an era defined by the need for sustainable development, Katsina State has taken a bold and strategic step forward. The Katsina Green Growth Agenda (KAGGA) is more than just a policy document, it is a transformative vision designed to align environmental resilience with economic growth.
ICT as a Catalyst for Climate Action: Turning Bytes into a Better Planet
TAKEAWAY Technology fuels transformation: ICT is the catalyst behind innovations that are reshaping how we fight climate change across energy, agriculture, waste, and education. Real-time data saves real-world ecosystems: From satellites to sensors, ICT tools give us the intelligence we need to protect forests, track emissions, and predict disasters. Digital solutions are accelerating the green economy: Clean tech startups, green data centres, and digital agriculture are making sustainability profitable and scalable. ICT bridges the global climate knowledge gap: Online platforms are giving communities access to environmental data, resources, and training. The future of climate action is digital: As ICT continues to evolve, its potential to drive systemic climate solutions is just beginning. INTRODUCTION Can climate change be hacked? Not in the literal sense, but ICT is doing something close to it. From satellites mapping deforestation in real time to AI models predicting floods weeks in advance, technology is fast becoming our most powerful ally for climate change mitigation and adaptation. In a world where every second matters, ICT transforms awareness into action and data into decisions. It’s not just about fighting climate change, it’s about staying one step ahead. BACKGROUND Climate change is no longer a distant threat, it’s a present reality. Rising temperatures, shrinking glaciers, and increasingly violent storms are a wake-up call. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) warns that we have until 2030 to cut global emissions in half or risk irreversible damage [1]. But while the threat looms large, a powerful solution lies in our hands in the form of mobile phones, internet access, and digital infrastructure. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) includes everything from software and sensors to broadband and blockchain. According to the Global e-Sustainability Initiative (GeSI), ICT has the potential to reduce global CO₂ emissions by 20% by 2030, even though the sector contributes only about 2-3% of emissions itself [2]. This is a leverage point: When deployed strategically, ICT is not just part of the solution; it amplifies the solution. Tracking Environmental Challenges, One Pixel at a Time Technology allows us to see what was once invisible. Satellite systems operated by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (United States) (NASA), the European Space Agency (ESA), and private firms can now detect forest loss, melting ice caps, and methane (CH4) leaks from space. These are critical tools in shaping climate policy and enforcement. For instance, Global Forest Watch uses satellite data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to monitor forests in real-time, alerting authorities of illegal logging within hours [3]. Meanwhile, the Environmental Insights Explorer by Google helps over 3,000 cities globally track building and transport emissions, helping mayors make data-driven climate decisions [4]. Without ICT, these insights would take months or never come at all. Smart Agriculture and Green Tech Agriculture, a major industry which emits greenhouse gases, is undergoing a digital revolution. ICT-powered tools such as precision farming, drone surveillance, and mobile weather forecasting are reducing input waste and increasing yields. In Kenya, applications like iCow and FarmDrive are helping smallholder farmers adapt to unpredictable weather by offering agricultural tips, weather updates, and access to microloans through mobile-based platforms. In India, sensors connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) are enabling farmers to control irrigation systems via SMS, conserving water while boosting food security. These solutions aren’t just reducing emissions, they are safeguarding our livelihoods and conserving the earth’s natural resources.. In the energy sector, smart grids are optimizing power distribution, cutting losses, and integrating renewables more efficiently. In fact, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA), smart energy systems powered by ICT could reduce electricity waste by up to 30% by 2030, aligning with global aligning with global climate goals[5]. Digital Empowerment and Education for Climate Climate literacy is no longer limited to scientists. Through mobile apps, virtual classrooms, and gamified learning platforms, ICT is making environmental education accessible and engaging. Applications like Earth Hero and Klima turn climate action into a personal mission, helping users calculate, reduce, and offset their carbon footprints. UN CC: Learn offers free online courses that have educated over 500,000 learners globally on climate resilience, green jobs, and adaptation strategies [6]. In vulnerable communities, ICT is also vital for early disaster warning systems. Text-based alerts on floods, wildfires, and storms have saved thousands of lives in countries like Bangladesh and the Philippines. That’s the power of a single byte in protecting entire populations. ICT and Circular Economy Innovation ICT is the backbone of the emerging circular economy, an economic model focused on designing out waste and keeping resources in use. Smart inventory systems, blockchain-powered product tracking, and mobile platforms for sharing or reusing goods are helping consumers and businesses close the loop. Companies like Too Good To Go, used widely in European countries such as Denmark, France, United Kingdom and Germany, help reduce food waste by using mobile applications that let consumers buy unsold food from restaurants, bakeries, and supermarkets at a discounted price; instead of throwing away perfectly good food at the end of the day. These businesses list it on the application, and users can reserve and pick it up at a lower cost. This way, food that would have gone to waste gets eaten, helping both the environment and people looking for affordable meals. Startup companies like Loop which launched in the United States, France and the United Kingdom, use digital platforms to manage reusable packaging systems, allowing consumers to return and reuse branded containers instead of relying on single-use packaging. Blockchain, in particular, is enabling transparency in carbon trading, e-waste recycling, and ethical sourcing [7]. These technologies make sustainability measurable, accountable, and profitable. Youth, Climate, and Digital Advocacy Young people are leading the digital charge for climate justice. Social media platforms have become megaphones for international movements like Fridays for Future and Stop Ecocide. With nothing more than a smartphone, youth activists from Africa to Asia are organizing protests, sharing climate stories, and pressuring world leaders into action [8]. Additionally, platforms like Youth Climate Lab and Connect4Climate use digital storytelling and
Harnessing Anaerobic Digestion For Biogas Production In Nigeria
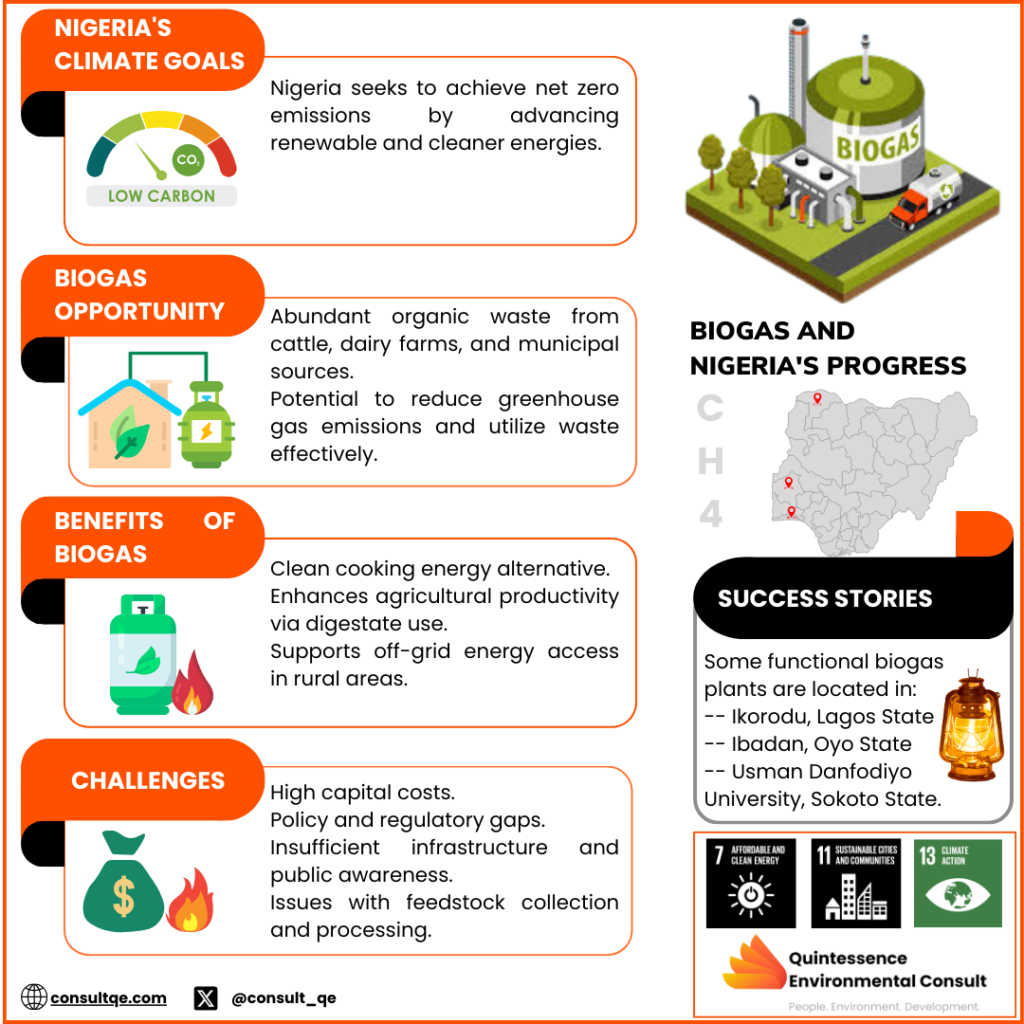
KEY TAKEAWAYS: Nigeria’s reliance on fossil fuel generated GHG emissionsof 100.389MT CO2 in the year 2022, ranking Nigeria to be 4th largest emitter of carbon in Africa. Anaerobic digesters are a great innovation for the country’s renewable energy options. Nigeria has abundant sources of organic waste suitable for biogas production. For instance cattle waste alone has the potential of yielding about 25.53 billion cubic meters of biogas about 169 541.66 MWh of electricity and 88.19 million tons of bio-fertilizer per annum. Biogas production offers diverse advantages, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, providing clean cooking energy, improving agricultural productivity through digestate use, and supporting off-grid energy access for rural communities. Various projects, such as the biogas plants in Ikorodu-Lagos State, Ibadan-Oyo State, and Usman Danfodiyo University-Sokoto State, demonstrate the feasibility of biogas technology. Biogas production in Nigeria faces barriers like high capital costs, policy and regulatory gaps, lack of infrastructure, limited public awareness, and challenges with feedstock collection and processing. 2. OVERVIEW Nigeria is heavily reliant on fossil fuels, primarily oil, because it is one of the largest oil producers in Africa, with proven reserves of 37.50 billion barrels and a production capacity of approximately 2.19 million barrels per day (mbpd).13 Majority of its government revenue and export earnings come directly from crude oil sales, making its economy heavily dependent on this resource. Heavy dependence on fossil fuels due to its economic value creates significant environmental concerns. Fossil fuels account for more than 65% of the country’s greenhouse gas emissions, with an alarming GHG emissions of 100.389MT CO2 in the year 2022, ranking Nigeria to be 4th largest emitter of carbon in africa.10 As Nigeria takes strides toward achieving its climate and energy transition goals under the Paris Agreement, reducing this dependency will be critical for sustainability and energy security. Biogas produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter offers a plethora of benefits for Nigeria’s energy mix; due to its renewable and clean energy resource. In this report, we will explore the transformative potential of harnessing this technology to play a pivotal role in waste management and renewable energy production, offering a sustainable solution to environmental issues in Nigeria. SO, WHAT IS ANAEROBIC DIGESTION? Let’s first talk about Organic Matter. Organic matter comprisesorganic compounds resulting from the remains of decomposed previously living organisms such as plants and animals, and their waste products. Major sources of organic material for anaerobic digestion include dairy manure, food processing waste, plant residues, municipal wastewater, food waste, fats, oils, and grease. Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a biotechnological process that uses the diverse population of microorganisms to decompose organic matter in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of biogas—a renewable energy source primarily composed of methane (CH₄). The biotechnological process involves four stages: Hydrolysis, acidogenesis, Acetogenesis and Methanogenesis.10 The transformation of organic matter into biogas unveils anaerobic digesters as an environmentally sustainable and eco-friendly energy solution. BACKGROUND INFORMATION Nigeria’s commitments under the Paris Agreement include achieving NetZero by 2060 and transitioning to clean energy sources.15 As such, Nigeria pledged in its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) to adopt bioenergy as an alternative clean energy fuel to enhance its Energy Transition agenda. This supports Nigeria’s Long-Term Strategy for decarbonization, aiming to reduce emissions by 20% below the projected baseline levels by 2030, with a conditional target of achieving a 47% reduction within the same timeframe.16 As Nigeria takes firm strides towards a greener and more sustainable future, biogas emerges as a reliable clean energy technology to facilitate Nigeria’s NDC commitment. CURRENT STATUS OF BIOGAS PRODUCTION IN NIGERIA Although biogas plants are not yet familiar in the Nigerian energy market, some substantial work has been done and work is still in progress on it. For instance: The Usman Danfodiyo University, Sokoto, has designed a plant that can produce 425 litres of biogas per day, sufficient for basic cooking needs. Biogas Plant for electricity generation through gas produced from co-digestion of cassava peels and cow dung at a factory in Ibadan, Oyo State In 2019, the biogas plant at Ikorodu Mini Abattoir, in Lagos State, was capable of converting organic waste through the installation of four 5,000-litre digester tanks, fed with digestible organic waste and concentrated wastewater from the abattoir. Biogas generated was used to power the abattoir for close to six hours daily. The project was carried out by the Lagos State government, Friends of the Environment (FOTE) and HIS Biogas.3 BTNL Nigeria’s project at the Maximum Security Custodial Centre in Port Harcourt focuses on producing organic fertilizer from waste. This initiative aims to convert waste generated within the facility into valuable organic fertilizer, promoting sustainable waste management and supporting agricultural productivity.8 In addition, various research works on the science and technology of biogas production have been carried out by various scientists in the country. The Biogas Practitioners Association of Nigeria (BPAN) and Nigeria Biogas Association (NBA) have attested that despite biogas technology has proven to be a reliable and sustainable source of clean energy that could enable an affordable, reliable and available alternative clean energy solution in Nigeria it has only gained little legislative adoption and implementation in the Nigerian energy policy. 13 SIGNIFICANCE OF BIOGAS PRODUCTION Biogas production offers multifaceted benefits that address energy, environmental, and socio-economic challenges. It’s also suitable for all the various fuel requirements in the household, agriculture and industrial sectors. For instance, domestically, it can be used for cooking, lighting, water heating, running refrigerators, water pumps and electric generators. Agriculturally, it can be used on farms for drying crops, pumping water for irrigation and other purposes. In industries, it can be used in small-scale industrial operations for direct heating applications such as in scalding tanks. 2 Biogas production offers multiple benefits: Providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, contributing to energy security and reducing reliance on non-renewable resources. Biogas systems capture methane emissions from decomposing organic waste that would otherwise escape into the atmosphere, reducing the overall greenhouse gas (GHG) impact, and significantly contributing to climate change mitigation. Anaerobic digestion
The Impact Of Deforestation On Nigeria’s Biodiversity: Causes And Consequences

KEY TAKEAWAYS Nigeria’s forests host an impressive array of biodiversity. Deforestation and biodiversity loss are deeply interlinked, with one exacerbating the other. As forests degrade, biodiversity declines, weakening natural resilience to climate change, and reducing crucial ecological services. Drivers of deforestation in Nigeria include agricultural expansion, logging (both legal and illegal), and urbanization. The projected consequences of deforestation in Nigeria are vital and must be eluded. Effective remediation requires strengthened policy enforcement, sustainable agricultural practices, alternative livelihoods, and community-driven conservation efforts. INTRODUCTION The National Strategy for Combating Wildlife and Forest Crime in Nigeria (2022-2026) underscores the critical importance of biodiversity preservation. Nigeria’s rich ecosystems support many species, including 864 species of birds, 117 amphibians, 203 reptiles, over 775 species of fish, 285 mammals, over 4,715 vascular plants, and probably many more unrecorded species (10). The overwhelming and escalating deforestation in Nigeria, threatens its biodiversity, tropical forests, and the rest of the many ecosystems and natural habitats. A key feature of Nigeria’s ecology is its large and burgeoning human population and the increasing pressure this population growth is putting upon the natural environment. THE SYNERGY OF BIODIVERSITY AND DEFORESTATION. The synergy between biodiversity and deforestation reflects an intricate, interdependent relationship with profound ecological implications. Biodiversity thrives in well-preserved forest ecosystems, where species diversity enhances ecological balance and resilience to environmental changes. However, deforestation disrupts these ecosystems, reducing biodiversity by destroying habitats, fragmenting populations, and altering natural processes. This loss of biodiversity, in turn, weakens the structure of forest ecosystems, reducing their ability to provide essential services like pollination, water regulation, climate regulation, and soil fertility (4). As species vanish, ecosystems become more vulnerable to invasive species and climate shifts, creating a feedback loop that accelerates forest degradation (8). Understanding this synergy highlights the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect biodiversity, which strengthens forest resilience and mitigates the long-term impacts of deforestation on both local and global ecological and economic systems. Protecting biodiversity is therefore essential not only for environmental integrity but also for sustaining the resources and processes on which human life depends. UNDERSTANDING THE INDELIBLE DEFORESTATION IN NIGERIA Deforestation has a severe impact on Nigeria’s biodiversity, leading to habitat loss, species extinction, and ecosystem imbalance. Forest ecosystems like the Cross River Rainforest host a unique range of species, including endangered animals such as the Cross River gorilla and Nigeria-Cameroon chimpanzee (10). As forests are cleared, these species lose critical habitats, resulting in population declines and increased vulnerability to extinction. (8). Deforestation in Nigeria is driven primarily by: Agricultural expansion: Smallholder farming and commercial plantations are major causes, accounting for extensive forest loss as the community’s clear land for food production and export crops like Palm oil and Cocoa. (5) Logging: The legal and illegal logging industry is driven by local demands for timber and firewood and international market demands. In Nigeria, firewood is still widely used as a primary source of energy, particularly for cooking. This practice not only contributes significantly to deforestation but also impacts air quality, posing severe health risks like respiratory issues. Furthermore, collecting firewood puts additional strain on forest ecosystems, which are already vulnerable due to other deforestation drivers, making it a critical environmental and health concern. (8). The accentuation of illegality in logging activities in the forest belts of Edo and Ondo States is worrisome, as it contributes more to the continuous deforestation taking place in Nigeria. Additionally, the price of charcoal has inflated from ₦1,000 and ₦4,000 to ₦7,500 and ₦9,000 per bag, depending on the location, due to the removal of fuel scarcity. This has put pressure on low-income earners as they have to source illegal means of timbering to acquire firewood. Urbanization: The large and burgeoning human population and the increasing pressure this population growth is putting upon the natural environment causes rapid urbanization and infrastructure projects in Nigeria, and this promotes forest clearing and displacement. Urban sprawl is particularly high around cities like Lagos and Abuja, intensifying pressure on nearby forests (11). Looking forward, if current deforestation trends continue, Nigeria may face severe ecological and economic repercussions. The loss of forest cover would exacerbate climate change effects by increasing carbon emissions and reducing natural carbon sinks, potentially intensifying droughts and extreme weather patterns (6). Biodiversity losses will likely impact agriculture, reducing crop pollination and soil fertility, and increasing vulnerability to pests, ultimately threatening food security and livelihoods. Many communities rely on forests for food, medicine, and fuel. Forest degradation results in decreased access to these resources, forcing people to adopt alternative, sometimes unsustainable practices. Furthermore, the decline in forest ecosystems may undermine Nigeria’s potential for ecotourism, reducing revenue from natural heritage sites and thereby inflating poverty. In the long term, these outcomes suggest a bleak future for biodiversity and underscore the need for urgent conservation actions to mitigate deforestation’s impacts. CHALLENGES AND REMEDIATION MEASURES Economically, sustainable forest management can support Nigeria’s ecotourism sector, providing jobs and generating revenue, while conserving resources essential for industries such as agriculture, medicine, and forestry. By halting deforestation, Nigeria can protect its rich biodiversity, support local economies, and build resilience to environmental challenges, ultimately fostering a healthier, more sustainable future. However, the issue of frail policy enforcement and governance (illegal mining of timber), economic pressures and poverty (lack of job opportunities), and lack of awareness and education, thrive as a great challenge for the remediation of the deforestation impact in Nigeria. (3) Although these challenges are of great concern, there are opportunities to remediate the deforestation impact on the Nigerian economy. Strengthening Policy and Enforcement Mechanisms: Developing robust legal frameworks, combined with adequate resources for enforcement, is crucial to controlling illegal logging and unsustainable land-use practices. Partnerships between the Nigerian government, NGOs, and international agencies can support policy-strengthening efforts and improve monitoring capabilities (2). Promoting Sustainable Agriculture and Alternative Livelihoods: Encouraging sustainable farming techniques, such as agroforestry, and providing alternative livelihoods for rural communities can reduce deforestation pressures. Programs that incentivize reforestation and community-based forest management can create economic benefits while conserving forests. (1) Education and Community Involvement:
