Reforming Nigeria’s Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining Sector: A Path to Sustainable Livelihoods
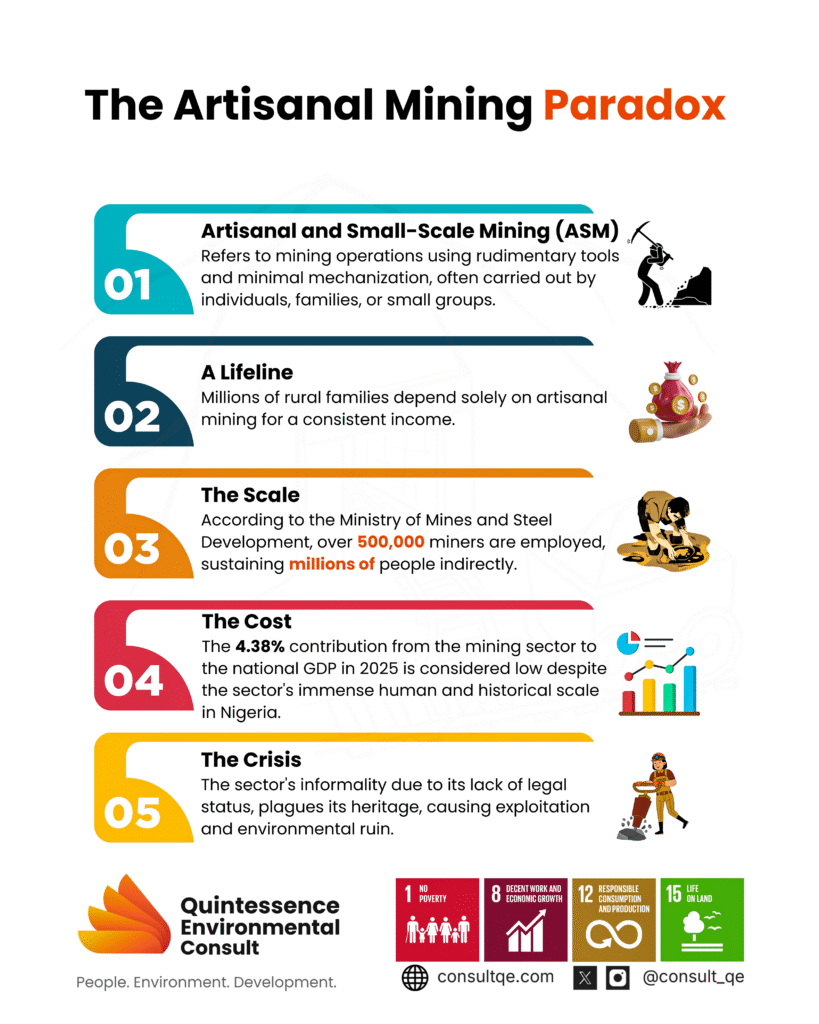
deposits of Plateau, Bauchi, and Kano, and the gemstone markets of Kaduna, ASM provides livelihoods where farming or other jobs are limited.
However, this lifeline comes with paradoxes. While ASM reduces rural poverty, supports households, and contributes to mineral output, it is also plagued by informality, unsafe practices, environmental degradation, and lost government revenue. Nigeria faces a crucial choice: continue to allow ASM to operate in the shadows, or reform it into a pillar of sustainable livelihoods and responsible mining.
The sector remains underdeveloped despite Nigeria’s mineral wealth across more than 500 locations in the 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory (FCT). The Nigerian Mining Corporation, once a leading producer, declined after the 1970s indigenization policy, and now contributes 4.38 per cent to the overall GDP in the first quarter of 2025, lower than the 5.47 per cent contribution recorded in the same quarter of 2024, according to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) latest GDP report.[14]
The underperformance stems largely from ASM-related challenges, including informality, weak regulatory oversight, insecurity, smuggling, and under-declaration of exported minerals.
Mine Closure and Land Rehabilitation: A Forgotten Chapter in Sustainability
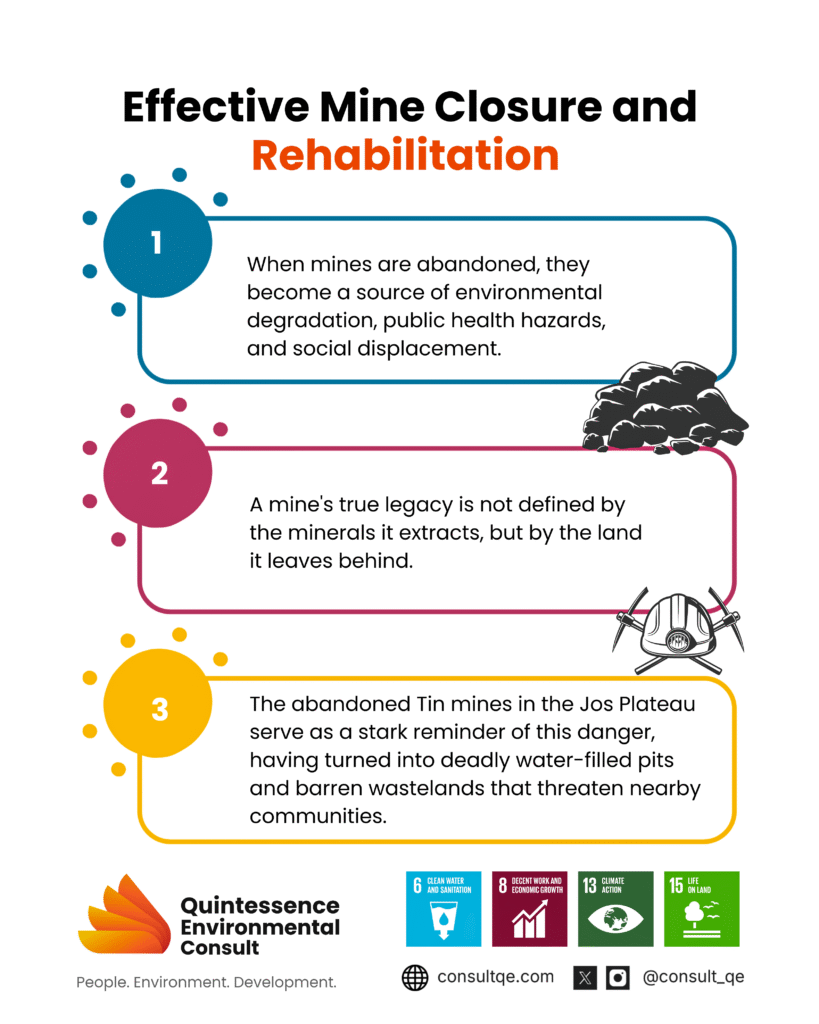
When conversations on sustainable mining arise, they often focus on responsible extraction, environmental safeguards, and community relations during active operations. Rarely, however, do they touch the crucial, final chapter of mining: “mine closure and land rehabilitation”, a chapter that determines whether the land will become a legacy of prosperity or a scar of neglect.
WHY IT MATTERS
For decades, mining in Nigeria and indeed in much of Africa, such as the Republic of Congo, South Africa, Ghana, etc, has been driven by the excitement of discovery and profit. Unfortunately, once minerals are depleted, many companies pack up, leaving behind degraded landscapes, toxic tailings, and polluted water bodies. Communities are left to deal with the aftermath: infertile soils, unsafe pits, and lost livelihoods. The abandoned tin mines in Jos, Plateau remain a stark reminder of the dangers of ignoring post-mining land use; many have turned into deadly water ponds or barren wastelands, posing environmental and public health risks [1].
In contrast, modern sustainable mining emphasizes not only “how we mine” but “what we leave behind”. Mine closure and land rehabilitation ensure that post-mining landscapes are safe, ecologically functional, and, where possible, economically useful.
Deforestation: A Critical Threat to Sustainable Water Resources

Nigeria, a nation rich in biodiversity, is facing the challenge of water scarcity. A significant, yet often underestimated, contributor to this is deforestation.
Forest ecosystems are integral in sustaining water resources by protecting river catchments, maintaining rainfall patterns, and filtering water naturally. (10) Forests significantly enhance soil moisture retention, minimizing surface runoff, storing considerable volumes of water within their canopy, and facilitating the gradual infiltration and percolation of water into the subsurface (3).
The continuous degradation and clearing of forest reserves in the country disrupts its natural hydrological processes, jeopardizing the sustainability of freshwater resources for millions (8).
Decarbonizing Nigeria’s Mining Sector: Strategies for Achieving Net-Zero Emissions

Mining has historically served as a cornerstone of Nigeria’s economic development, with notable resource extraction activities ranging from Tin in Jos and Gold in Zamfara to Lithium in Nasarawa. The country’s substantial endowment of mineral resources presents significant economic opportunities; however, these benefits are accompanied by critical environmental challenges. The mining sector contributes considerably to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily through the combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, and unsustainable operational practices.
The Environmental Cost Of Illegal And Unregulated Granite Quarrying In Nigeria

KEY TAKEAWAYS Illegal Granite Quarrying Is Environmentally Devastating: Unauthorized quarrying is responsible for widespread deforestation, air and water pollution, and irreversible land degradation across several Nigerian states. Health and Safety Risks Are Alarming: Unregulated granite extraction releases harmful dust (PM10), contributing to respiratory illnesses like asthma and sinusitis among nearby residents and quarry workers. Communities and Ecosystems Are Under Threat: Case studies from Abeokuta, Abuja, Edo, and Ebonyi reveal how quarrying disrupts ecosystems, reduces water quality, and destroys farmlands, threatening food security and biodiversity. Earth Tremors in Abuja Highlight Deeper Geotechnical Risks: The recent seismic activities in the Federal Capital Territory may be linked to unregulated blasting, underscoring the need for proper environmental and geological assessments. Sustainable Solutions and Community Action Are Urgently Needed: Stronger regulations, mandatory environmental impact assessments, rehabilitation of quarry sites, and active community engagement are essential to mitigate the environmental crisis. INTRODUCTION A quarry is a large, open excavation site on the earth’s surface where natural resources like stone/rock, gravel, sand, or minerals are extracted. Granite is a hard, coarse-grained igneous rock composed mainly of quartz, feldspar, and mica. It forms naturally when molten magma slowly cools and solidifies deep beneath the Earth’s surface. Granite quarrying is the process of extracting granite rock from the earth through open-pit mining methods. For many years, it has served as an important source of construction materials supply, employment and revenue, especially in developing countries like Nigeria, which are endowed with abundant granite deposits. Nigeria’s vast granite reserves have long fueled its construction and mining industries. From road construction to building skyscrapers, granite is an essential raw material. However, behind this booming industry lies a dark reality: illegal granite quarrying is wreaking havoc on the environment, leading to various impacts such as deforestation, soil erosion, water pollution, and air contamination. This article explores the environmental cost of illegal granite quarrying in Nigeria, shedding light on the consequences, key case studies, and the urgent need for sustainable mining practices. UNDERSTANDING ILLEGAL AND UNREGULATED GRANITE QUARRYING IN NIGERIA Illegal quarrying refers to the unauthorized extraction of granite without government approval, environmental impact assessments, and adherence to mining regulations. Many of these operations are run by small-scale miners or criminal syndicates, often exploiting rural communities for labour. The lack of oversight means these quarries operate recklessly, leading to widespread environmental degradation. Abeokuta city in Ogun State, for example, known for its abundant granite resources, is flourishing with illegal quarrying, which has caused significant health and environmental damage. A study by Oguntoke Olusegun (2009) shows that granite quarrying in Abeokuta has led to elevated levels of suspended particulate matter (PM10), posing serious health risks to nearby residents and quarry workers. Common issues include nasal infections, asthma, cough, and sinusitis. Similarly, in the Federal Capital Territory (Abuja) and its surrounding areas, rapid urbanization has increased demand for granite, leading to uncontrolled quarrying activities in areas such as Mpape 6, which threaten both the environment and local communities. Another example is granite quarrying in Edo North, Nigeria, where daily activities such as drilling, blasting, crushing, and transporting materials have a significant impact on the environment. These operations contribute to air and noise pollution, water contamination from runoff, and land degradation. With multiple active quarries per community, a study by Okolie K. C. 2021 confirms that quarrying practices have adverse environmental impacts. In Afikpo, Ebonyi State, the environmental impact of rock quarrying goes beyond just the physical destruction of the land. It also affects the quality of air and water in the area. The dust and debris from the quarrying process can contaminate the air and water, making them unsuitable for human consumption 3. ENVIRONMENTAL CONSEQUENCES OF ILLEGAL AND UNREGULATED GRANITE QUARRYING Deforestation and Habitat Loss Illegal quarrying often requires clearing large tracts of land, leading to deforestation. The loss of vegetation disrupts ecosystems, endangers wildlife, and contributes to climate change. A study by Adedeji et al. (2020) in Odeda, Ogun State, observed a significant decline in light forest cover from 637.28 hectares in 1984 to 326.52 hectares in 2014, attributed to quarrying activities. This represents nearly a 50% reduction over 30 years. Similarly, Akanwa et al. (2017) reported a 35.2% vegetation cover loss in Ivo Local Government Area, Ebonyi State, due to intensive quarrying operations. Soil Erosion and Land Degradation The process of quarrying begins with the removal of vegetation and topsoil. In legal operations, this is done with care and often includes plans for rehabilitation. However, illegal quarrying strips the land bare without any concern for restoration. Once the protective topsoil is gone, the land becomes exposed to wind and water erosion. This leads to the rapid washing away of soil nutrients essential for farming and biodiversity. Several communities have watched their fertile lands slowly transform into barren, rocky outcrops. Quarry pits are left open and untreated, turning into erosion channels and death traps. Rainfall accelerates this degradation, creating gullies and reducing the land’s capacity to support crops or vegetation. Water Pollution and Scarcity During quarrying, overburden removal, drilling, blasting, and rock crushing release large volumes of silt, dust, and chemicals into the environment. Without proper drainage or containment systems, runoff from quarry sites flows into nearby rivers, streams, and groundwater sources. This runoff carries fine particles, heavy metals, and sometimes explosive residues, which degrade water quality and harm aquatic ecosystems. In many rural communities that rely on surface and shallow groundwater for drinking, washing, and farming, this pollution leads to outbreaks of waterborne diseases, loss of fish populations, and reduced access to safe water. The disruption of natural drainage patterns also reduces groundwater recharge, intensifying water scarcity during dry seasons. Air Pollution and Public Health Risks One of the most visible effects of illegal quarrying is the release of large amounts of dust and particulate matter (PM10) into the air. This occurs during blasting, crushing, and the constant movement of heavy trucks. Without dust control systems like sprinklers or barriers, standard in regulated sites, these pollutants are freely dispersed into nearby communities. Residents
