Beyond Smart Grids: Unpacking the Next Wave of Digitalization in Nigeria’s Energy Sector
Nigeria stands at a pivotal moment in its energy transition. While the conversation around smart grids has laid a crucial foundation, the next wave of digitalization promises even more profound transformations. We are talking about a future where Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, digital twins, and edge computing converge to create an energy ecosystem that is not just smart, but also predictive, resilient, and highly efficient. As Nigeria grapples with the dual challenge of expanding energy access and ensuring sustainability, these advanced digital tools are no longer futuristic concepts but essential enablers for progress.
This evolution is about using deeper intelligence to solve persistent problems, such as high energy losses and grid instability, and unlocking new opportunities for consumers and the economy.
Smart Energy Solutions: How AI and IoT Are Revolutionizing Energy Efficiency in Nigeria

Takeaways: AI and IoT-Enabled Meters Reduce Energy Wastage: Smart energy management systems use AI and IoT to track and optimize energy use, cutting costs for consumers. Real-Time Monitoring Saves Money: IoT-enabled smart meters can help Nigerian households and businesses monitor and reduce electricity consumption. Improved Grid Stability: AI-driven energy distribution can help reduce blackouts and improve the reliability of Nigeria’s power grid. Smart Energy Is the Future: As AI and IoT adoption grows, integrating these technologies into Nigeria’s energy sector can enhance sustainability and economic efficiency. Did you know that intelligent automation can cut energy waste by up to 30%? Amid rising electricity tariffs and persistent grid instability, adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) for energy efficiency is no longer an option—it’s a necessity for Nigeria. In Nigerian homes and businesses, energy bills are soaring, with Band A customers (those with 20 + hours of daily electricity access) paying up to ₦209.5 per kilowatt-hour (kWh) (NERC, 2024). For many, this electricity cost per kWh is unsustainable. However, individuals and businesses can track, analyze, and reduce their power consumption through AI-driven energy optimisation and IoT-enabled smart meters. These technologies ensure that every watt counts, significantly lowering electricity costs and enhancing grid stability by reducing the energy demand on the national grid. The Rising Cost of Energy in Nigeria: A Call for Smarter Solutions Energy prices in Nigeria are driven by factors such as currency devaluation, rising fossil fuel prices and reliance on outdated infrastructure. Many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) still rely on inefficient energy sources like diesel generators, which are costly and environmentally harmful. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), AI-driven energy efficiency solutions could reduce global energy demand by 40% by 2040. For Nigeria, this presents an opportunity to alleviate energy poverty while maximizing existing resources. Benefits of AI and IoT: Energy Consumption Globally, AI and IoT have demonstrated transformative potential in energy optimization. In Nigeria, these technologies align with national energy security objectives and multiple Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): AI-Driven Energy Optimization AI-powered analytics can predict energy usage patterns and automate power distribution. Businesses and homes using smart energy systems powered by AI can: Reduce electricity waste by identifying inefficient appliances. (Supports SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy, SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production) Automate power usage based on demand, reducing unnecessary consumption. (SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) Predict peak demand periods and adjust energy usage accordingly. Enhance energy storage efficiency by optimizing battery charging cycles. (SDG 13: Climate Action) Improve fault detection in electrical networks and prevent system failures. (SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities) IoT-Enabled Smart Energy Management IoT sensors and smart meters provide real-time data on power consumption, helping consumers make informed decisions. Benefits include: Remote Monitoring: Homeowners and businesses can track their energy usage via mobile apps. Automated Power Adjustments: Smart thermostats and lighting systems adjust based on usage patterns. Fault Detection: IoT-enabled systems can detect faulty appliances that waste energy. Grid Load Balancing: Smart meters can communicate with the power grid, helping utilities distribute electricity efficiently. (SDG 7) Demand Response Systems: AI and IoT can help regulate energy consumption during peak hours. Case Studies: Global and Local Applications Globally, AI-powered smart energy grids have been adopted to enhance efficiency. Some successful implementations include: Kenya’s Smart Metering Project: Kenya Power adopted AI-driven smart metering systems across the country. The system uses advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) that sends real-time data to the utility about power usage, which allows for immediate detection of anomalies or irregularities, such as power theft. India’s AI-Powered Grid Management: The Indian government, in collaboration with energy providers like the Power Grid Corporation of India (PGCIL), deployed an AI-based grid management system. The system uses machine learning algorithms to analyze historical grid data and real-time data from sensors placed throughout the grid. South Africa’s IoT-Based Demand Response System: South Africa’s Eskom and various local municipalities began using an Internet of Things (IoT)-based demand response system to manage electricity consumption efficiently. The system integrates AI with IoT sensors placed in homes, businesses, and industrial facilities. United States’ Smart Home Integration: U.S. utilities, including Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) and Con Edison, have rolled out AI-driven home energy management systems that are integrated with smart home devices, such as thermostats, lighting systems, and appliances, to optimize energy use. Germany’s AI-Powered Renewable Energy Forecasting: TenneT, Germany’s energy company, implemented an AI-driven renewable energy forecasting system to improve the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources. The system uses machine learning to predict solar and wind power generation based on weather patterns and historical data. (Supports SDG 13) In Nigeria, early adopters of smart energy solutions are already seeing results. For example, Nigeria’s Primelink SmartLink Project has demonstrated the potential for technology-driven supply chain transformation. By integrating AI, IoT, and blockchain, the project achieved a 20% reduction in logistics costs and a 30% improvement in delivery reliability. (Lawrence, 2025). Some businesses that have integrated IoT-powered energy tracking systems report up to a 20% reduction in electricity bills (Yahya M.S. et al. 2023). Table: AI and IoT Solutions for Different Consumer Types in Nigeria Consumer Type Smart Energy Solutions Examples Homeowners Smart meters, AI-powered energy optimization, smart appliances Smart thermostats, automated lighting, real-time monitoring apps Small Businesses (SMEs) IoT-based energy tracking, smart office equipment Energy-efficient printers, automated air conditioning systems Large Corporations AI-driven energy analytics, IoT-enabled monitoring Smart grid integration, AI-based load balancing Agriculture Smart irrigation, solar-powered sensors, AI-driven climate control IoT-powered drip irrigation and automated greenhouse management (SDG 2: Zero Hunger) Retail/Commercial Smart HVAC systems, AI-powered billing, demand response tech Smart refrigeration, automated lighting controls Public Sector Smart street lighting, AI-powered grid management Solar-powered traffic lights, motion-sensor lighting in public buildings Challenges and Opportunities for AI and IoT Adoption in Nigeria Nigeria’s National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA) has announced plans to establish research centers dedicated to emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and robotics across the country’s six geopolitical zones. NITDA will create innovation
The Industrial Revolutions and the Role of Energy: A Pathway for Nigeria’s Sustainable Development
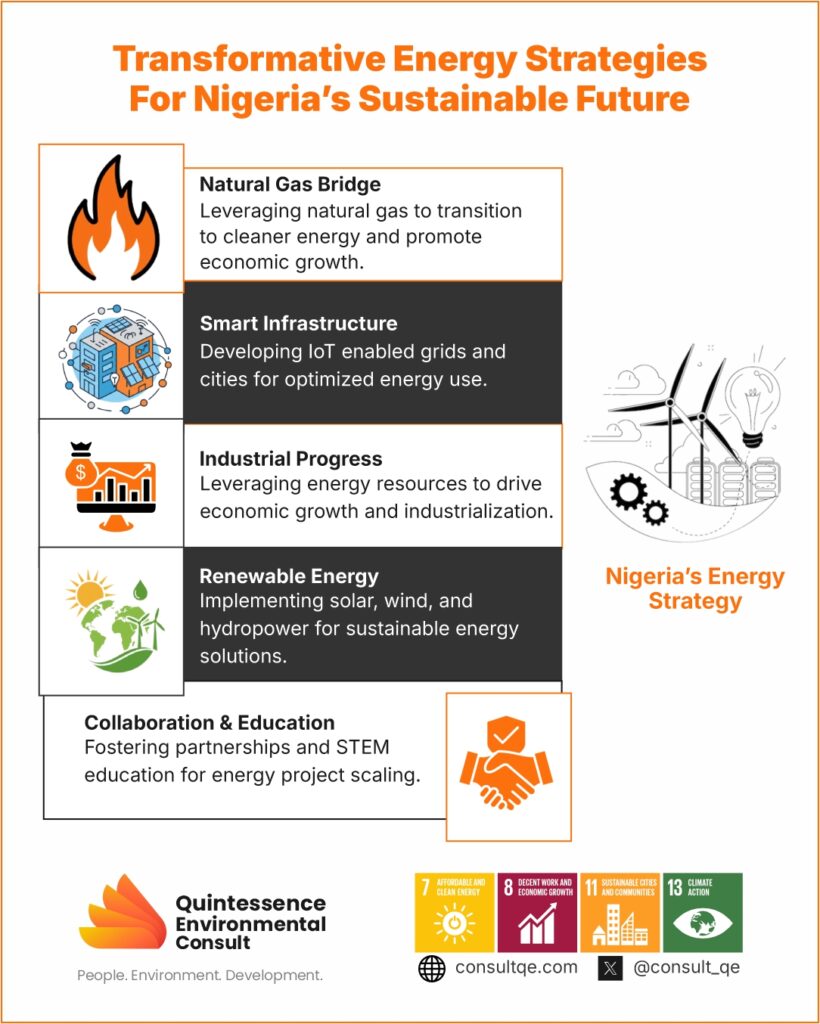
Key Takeaways: Energy Drives Industrial Progress: Every industrial revolution has been powered by transformative energy sources. Nigeria must leverage its energy resources—natural gas and renewables—to fuel economic growth and industrialization. Natural Gas is a Bridge to Sustainability: Nigeria’s vast natural gas reserves can address energy poverty, power industries, and reduce reliance on dirtier fuels, aligning with SDG 7 (Clean Energy) and SDG 8 (Economic Growth). Renewables are Nigeria’s Future: Solar, wind, and hydropower offer clean, decentralized energy solutions, supporting SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 9 (Innovation and Infrastructure). Smart Infrastructure is Essential: IoT-enabled smart grids and smart city projects can optimize energy use and support tech-driven industries, contributing to SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities). Collaboration and Education are Key: Public-private partnerships and investments in STEM education are crucial for scaling energy projects and building a skilled workforce, aligning with SDG 4 (Quality Education) and SDG 17 (Partnerships). Introduction Human progress has been profoundly shaped by industrial revolutions, each driven by transformative energy sources and technologies. From the steam engine to artificial intelligence, these revolutions have redefined economies, societies, and global power dynamics. For Nigeria, a nation rich in resources but grappling with energy poverty and economic challenges, understanding these revolutions offers a roadmap for sustainable development. This blog post explores the four industrial revolutions, the pivotal role of energy in each, and how Nigeria can strategically position itself to harness these lessons for growth and innovation. The Evolution of Industrial Revolutions and Energy’s Central Role The First Industrial Revolution (late 18th to early 19th century) marked the transition from agrarian economies to industrialized societies, powered by coal and steam engines. This era introduced mechanized production, revolutionizing industries like textiles and transportation. Coal became the backbone of economic growth, enabling mass production and the expansion of railways and factories. For example, the United Kingdom’s use of coal-powered steam engines not only transformed its economy but also set the stage for global industrialization. The Second Industrial Revolution (late 19th to early 20th century) was defined by the advent of electricity, the internal combustion engine, and oil. Electricity became the lifeblood of industries and households, while oil transformed transportation and logistics. Henry Ford’s assembly line, powered by electricity, revolutionized manufacturing, making automobiles affordable and accessible. This period laid the foundation for modern industrial economies, demonstrating how energy accessibility can drive innovation and economic growth. The Third Industrial Revolution (late 20th century) brought digitalization, computers, and the internet, ushering in the Information Age. Energy demand shifted towards oil, natural gas, and nuclear power, with growing awareness of environmental sustainability. For instance, the rise of Silicon Valley was fueled by reliable energy systems that powered data centers and communication networks. This revolution highlighted the importance of energy in enabling technological advancements and global connectivity. The Fourth Industrial Revolution (21st century) is characterized by artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and a strong emphasis on sustainability. Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydrogen are replacing fossil fuels, enabling smart grids, electric vehicles, and energy-efficient technologies. Countries like Germany, with its Energiewende (energy transition) policy, are leading the way in integrating renewables into their energy systems, demonstrating how innovation and sustainability can go hand in hand. Nigeria’s Opportunity: Learning from the Past, Building for the Future Nigeria stands at a critical juncture, with the potential to leverage its abundant natural resources and youthful population to drive sustainable development. By drawing lessons from the industrial revolutions, Nigeria can address its energy challenges and position itself as a leader in Africa’s economic transformation. Harnessing Natural Gas as a Transition Fuel: Nigeria boasts one of the largest natural gas reserves globally, yet much remains untapped. Natural gas can serve as a bridge fuel, providing a cleaner alternative to coal and oil while addressing the country’s energy deficit. For example, the Nigerian Liquefied Natural Gas (NLNG) project has already shown how gas can be monetized and used to generate electricity. Expanding such initiatives can stabilize electricity supply, power industries, and create jobs, aligning with SDG 7 (Affordable and Clean Energy) and SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth). Embracing Renewable Energy: With abundant sunlight, wind, and hydropower potential, Nigeria is well-positioned to transition to renewable energy. The Nigeria Electrification Project (NEP), which aims to provide off-grid solar power to rural communities, is a step in the right direction. By investing in renewable energy projects and incentivizing private sector participation, Nigeria can build a sustainable energy ecosystem that supports economic growth and environmental preservation, contributing to SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure). Building Smart Infrastructure: The Fourth Industrial Revolution emphasizes the importance of smart technologies and infrastructure. Nigeria can adopt IoT-enabled smart grids to optimize energy distribution, reduce waste, and improve access. For instance, the Lagos Smart City Project aims to integrate technology into urban planning, including energy management. Such initiatives can enhance energy reliability and resilience, supporting the growth of tech-driven industries and urban development, in line with SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities). Fostering Innovation and Education: A skilled workforce is essential to navigating the complexities of modern industrial and energy systems. Nigeria must prioritize STEM education and vocational training to build a talent pool that drives innovation. Programs like the African University of Science and Technology (AUST) in Abuja are already equipping students with the skills needed for the Fourth Industrial Revolution. This focus on education aligns with SDG 4 (Quality Education) and SDG 9. Encouraging Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between the government, private sector, and international organizations is crucial to scaling energy projects and industrial initiatives. For example, the Azura-Edo Power Plant, a public-private partnership, has added significant capacity to Nigeria’s electricity grid. Such collaborations can mobilize resources, share risks, and ensure the successful implementation of large-scale infrastructure projects, contributing to SDG 17 (Partnerships for the Goals). Conclusion The industrial revolutions have demonstrated that energy is the cornerstone of economic transformation. For Nigeria, the path to prosperity lies in strategically leveraging its energy resources, embracing renewable technologies, and fostering innovation. By learning from the past and adapting to the demands of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, Nigeria can unlock its immense potential, drive sustainable development, and emerge as a leader in Africa’s industrial and energy landscape. The time
Transforming Nigeria’s Power Grid: Pathways to Sustainable and Reliable Transmission and Distribution Infrastructure
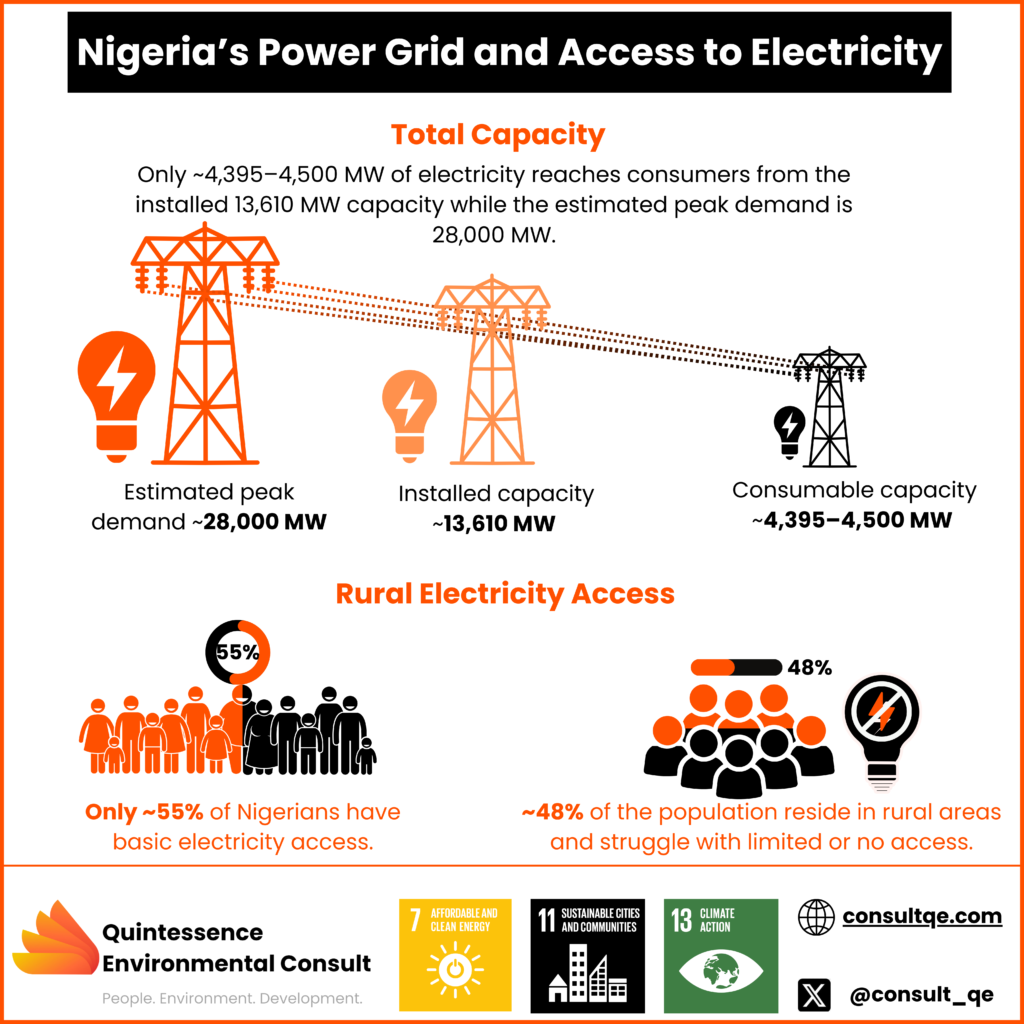
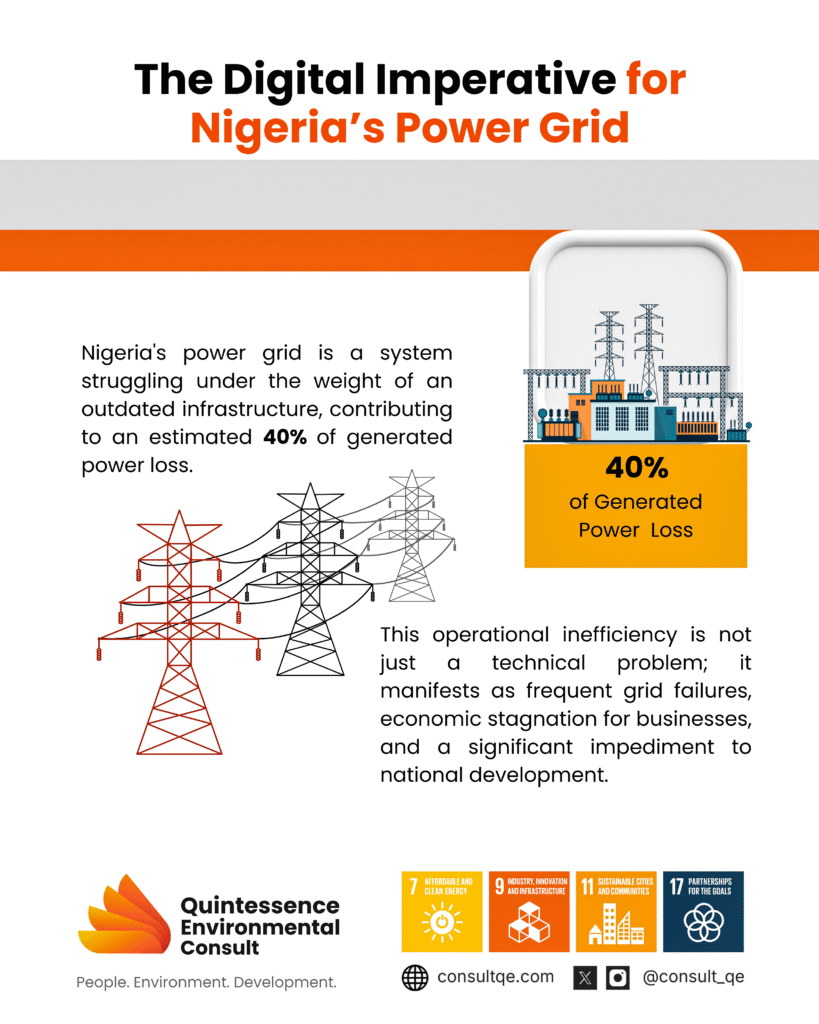
KEY TAKEAWAYS: Aging Power Grid with High Losses: Nigeria’s power grid is outdated and loses about 40% of generated power due to inefficiencies, far above the global standard of 8-12%, limiting reliability and revenue. Demand for Investment: Nigeria’s T&D system needs approximately $1.5 billion annually for a decade to modernize, but government appropriation alone won’t meet this demand, highlighting the importance of private investment. Microgrids as a Rural Solution: Decentralized microgrids can cut power costs by up to 40% for rural communities, providing reliable, local energy and easing pressure on the main grid. Smart Grids for Efficiency: Smart grid technology could reduce power losses by 30%, enhance grid resilience, and support the integration of renewables, creating a more adaptable power system. Need for Public-Private Partnerships and Policy Reform: Strategic public-private partnerships and streamlined regulations are essential to attract investment and ensure reliable, quality service across Nigeria’s power infrastructure. INTRODUCTION Imagine a Nigeria where electricity is constant—no more sudden blackouts, no more generators roaring through the night, and no more limits on economic growth due to unreliable power supply. For most Nigerians, this remains a distant dream as our power sector continues to grapple with significant challenges, especially in its transmission and distribution (T&D) infrastructure. Yet, precisely this infrastructure is key to unlocking reliable power and unleashing Nigeria’s full potential. This post explores the current state of Nigeria’s electrical grid, its critical challenges, and actionable strategies to advance towards modernized and sustainable electrification. Utilizing data from industry analyses and effective global frameworks, we have outlined a progressive sustainable solution, patterned for Nigeria’s energy future. NIGERIA’S POWER GRID AND ACCESS TO ELECTRICITY Nigeria’s current power grid ranks among the least reliable worldwide, with technical and operational inefficiencies significantly impeding electricity access. Only 55% to 60% of Nigerians have basic access to electricity. Nevertheless, even this limited coverage is often interrupted due to unreliable infrastructure and frequent outages. Despite a reported installed generation capacity of 13,610 MW, grid inefficiencies mean that only about 4,395–4,500 MW reliably reach consumers, far short of the estimated peak demand of 28,000 MW. Long, centralized transmission lines lead to high technical losses, particularly as they often exceed capacity, creating bottlenecks that result in regular “grid collapses” under high demand (6). The Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission (NERC) reports the systemic issues of the power sector, including outdated equipment and lack of investment in transmission and distribution infrastructure. As the grid struggles to meet current demand, a decentralized approach is becoming more attractive. Decentralized systems, including renewable microgrids and mini-grids, could alleviate strain on the central grid while providing reliable power to remote areas. (3). MAJOR CHALLENGES IN NIGERIA’S TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS Aging Infrastructure and Chronic Underinvestment The infrastructure of Nigeria’s transmission and distribution (T&D) is outdated, with decades-old lines, transformers, and substations that are underfunded and therefore operate far below optimal capacity. The World Bank estimates that Nigeria requires around $1.5 billion annually for the next ten years to modernize its T&D network adequately. Despite this need, investment levels have remained insufficient, as the power sector relies on inconsistent government budget allocations and occasional funding through partnerships, falling short of the comprehensive capital required for critical upgrades (11). High Power Losses, Both Technical and Non-Technical Nigeria experiences some of the highest transmission and distribution losses globally, with an estimated loss rate of 40% compared to the global standard of 8-12% (12). These losses stem from both technical issues—such as aging infrastructure and extended transmission distances—and non-technical issues, including electricity theft and inaccurate billing practices. Studies show that these inefficiencies severely reduce revenue, limiting the utilities’ ability to reinvest in essential grid upgrades and maintenance, thereby perpetuating a cycle of poor reliability and service limitations. (1) Limited Access for Rural Communities Approximately 48% of Nigeria’s population resides in rural regions, where access to the main electricity grid remains limited or unavailable. Extending the transmission and distribution (T&D) network to these remote areas is challenging, requiring an estimated $8 billion investment as estimated by the Rural Electrification Agency (REA). This considerable cost and the logistical barriers in reaching these underserved communities have hindered electricity access and slowed local economic development in areas where power is urgently needed (12). Policy and Regulatory Complexities Nigeria’s regulatory environment remains complex and often unpredictable, deterring private investment. Reforms intended to attract private players often falter due to inconsistent policies, such as sudden tariff changes and contract delays. For example, a 2019 tariff increase meant to improve cost recovery was repeatedly postponed, creating uncertainty. These shifts make investors wary, stalling the long-term projects crucial for strengthening Nigeria’s T&D infrastructure.(6) PATHWAYS TO TRANSFORM NIGERIA’S TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION INFRASTRUCTURE Investing in Smart Grid Technology Smart grids use digital monitoring and automation to manage power distribution more effectively, allowing for faster responses to fluctuations and reducing blackout risks. This technology reduces energy loss, enhances grid resilience, and allows for better integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the power supply scheme. Smart grids also reduce technical and non-technical losses by up to 30%. Furthermore, renewable integration through smart grids can support Nigeria’s decarbonization goals, aligning with commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 47% by 2030 as per its Paris Agreement obligations (2). Though achieving these improvements will require significant capital, partnerships with international organizations and private stakeholders can help Nigeria develop a more sustainable, reliable power infrastructure. Expanding Decentralized and Microgrid Solutions Microgrids offer an effective solution for powering Nigeria’s rural and remote areas, operating either independently or alongside the national grid. Microgrids are often used to power remote or rural areas where extending the central grid is not feasible and they can deliver cleaner and more cost-effective electricity. They rely on distributed energy resources (DERs), such as small-scale solar panels, wind turbines, and batteries, providing localized, reliable, and resilient power. Research by the Rocky Mountain Institute and Nigeria’s Rural Electrification Agency indicates that implementing microgrids could cut electricity costs for rural households by roughly 40%, while greatly enhancing their energy supply’s
Energy Efficiency: A Hidden Energy Source for Nigerians Amid Rising Energy Costs
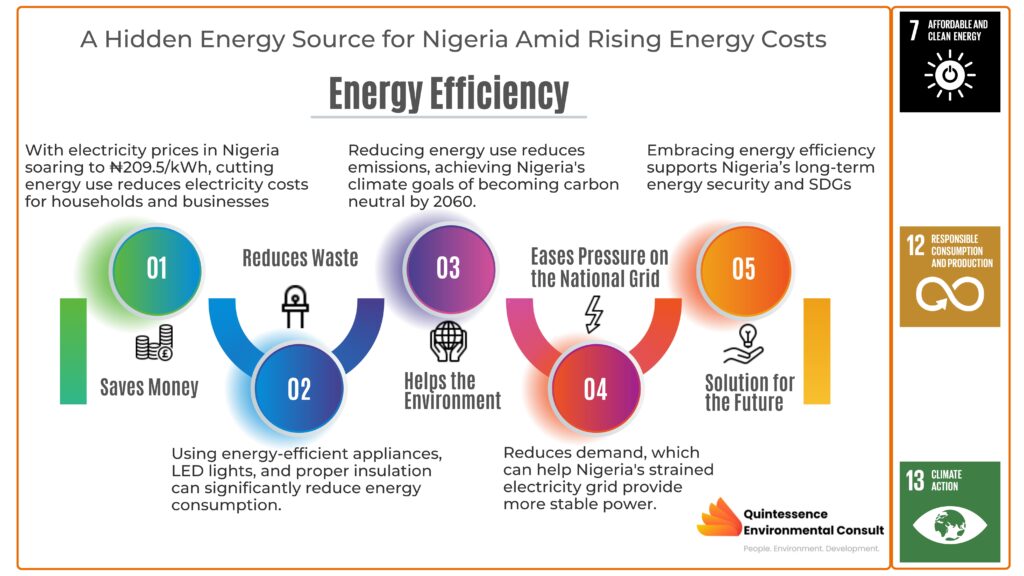
Takeaways: Energy Efficiency Saves Money: With electricity prices in Nigeria rising to ₦209.5 per kWh, using less energy can help lower electricity bills for households and businesses. Energy Efficiency Reduces Waste: Simple changes like using energy-efficient appliances, LED lights, and proper insulation can significantly reduce energy consumption. It Helps the Environment: By reducing energy use, we also cut down on emissions, helping Nigeria achieve its climate goals, like becoming carbon neutral by 2060. Eases Pressure on the National Grid: Energy efficiency reduces demand, which can help Nigeria’s strained electricity grid provide more stable power. Energy Efficiency Is a Solution for the Future: Embracing energy efficiency now will not only save money but also support Nigeria’s long-term energy security and sustainable development goals. Did you know? Did you know that saving energy can be just as powerful as generating it? Think of it this way: every kilowatt of electricity we don’t waste is a kilowatt we don’t need to produce. A brief survey of opinions around the suburbs of Abuja show that many homeowners spend an average of N70,000.00 per month to meet their energy needs. For businesses and other heavy power users, the figure is worse, with many closing shops. Efficient energy use: However, by using energy more efficiently, we’re not just reducing our bills—we’re also reducing the demand on power plants and the overall strain on the electricity grid. It’s like plugging a leak in a water pipe: the more we prevent waste, the less we need to pump. In essence, the energy we save can have just as much impact as the energy we create, helping to make our resources stretch further and work smarter for us. Rising energy prices in Nigeria are driven by various macroeconomic factors, such as fluctuating foreign exchange rates and escalating gas prices. According to the Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission (NERC), by July 2024, Band A customers, who are guaranteed 20-24 hours of electricity daily, were paying as much as ₦209.5 per kWh. For many, this hefty cost has become a significant financial burden. With energy costs climbing, Nigeria’s journey toward energy security and economic sustainability should focus on more than just increasing supply—it must prioritize efficiency as well. The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that energy efficiency could reduce global energy demand by 40% by 2040. In Nigeria, this approach could serve a dual purpose: cutting emissions while also lowering electricity bills and easing pressure on the overstretched national grid. Rising electricity tariff: Electricity tariff in Nigeria has been on a steady rise due to external factors, including the devaluation of the naira and increasing gas prices. As mentioned earlier, Band A consumers now face tariffs of up to ₦209.5 per kWh. In this context, inefficient energy use only exacerbates the financial strain on households and businesses. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are especially impacted, as they account for about 70% of industrial jobs and 50% of manufacturing output. Many SMEs still depend on inefficient energy sources, such as diesel generators, which not only inflate operational costs but also harm the environment. By embracing energy-efficient practices, SMEs can cut their energy expenses and contribute to Nigeria’s transition to a cleaner, net-zero future. Energy efficiency options: So, what is energy efficiency? Simply put, it means using less energy to accomplish the same tasks, thus cutting down on waste. Small, simple changes—like switching to energy-efficient appliances, using LED lighting, and improving home insulation—can make a big difference. Table 1 shows examples of energy efficiency measures that can be taken by different sectors of the economy. Consumer Type Energy Efficiency Measures Examples Homeowners Switch to energy-efficient lighting and appliances,improve insulation, and adopt solar/inverter systems. LED bulbs, solar-powered lighting, energy-efficient refrigerators. Small Businesses Use energy-efficient office equipment, LED lighting, and consider solar for power backup. Solar-powered POS, LED office lighting, inverter-based air coolers. Large Corporations Conduct energy audits, upgrade machinery, and invest in renewable energy like solar or cogeneration systems. DC motors, solar panels, energy-efficient HVAC systems. Agriculture Solar irrigation, biogas digesters, energy-efficient milling machines. Drip irrigation systems, energy-efficient greenhouses. Use solar-powered pumps, biogas, and energy-efficient processing machines. Implement precision farming to optimize energy and water use, and use energy-efficient greenhouse technology Retail/Commercial Switch to energy-saving HVAC, LED lighting, and smart meters. Adopt solar for kiosks or small shops. Retrofit building facades with reflective materials to reduce cooling loads. Solar kiosks, smart thermostats, energy-efficient refrigeration. Reflective building facades. Public Sector Install energy-efficient lighting, HVAC, and solar backup systems in institutions like schools and hospitals. Adopt net-zero energy building designs for new public projects LED in schools, solar-powered hospital backups, motion-sensor office lights. Net-zero energy buildings Table 1: Showing Energy Efficiency Measures by Consumer Type in Nigeria By adopting these measures, Nigerian consumers can not only reduce their energy consumption but also lower their energy bills. The World Bank’s Nigeria Power Sector Recovery Plan emphasizes the role energy efficiency can play in stabilizing the country’s electricity sector. By cutting down demand, energy efficiency lightens the load on the national grid, which is already stretched thin. Other benefits: Beyond the obvious cost savings, energy efficiency is critical for Nigeria’s environmental goals. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) outlines that Nigeria aims to reach carbon neutrality by 2060. Energy efficiency can be a key driver in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, helping the country align with global sustainability targets. In fact, energy efficiency holds the potential to transform Nigeria’s energy landscape especially if SMEs embrace it. As energy prices continue to rise, it provides a practical, cost-effective solution that benefits both consumers and the environment. For households and businesses, embracing energy-efficient practices can significantly reduce energy bills, relieving some of the financial burden caused by high tariffs. Furthermore, by reducing overall electricity demand, energy efficiency can help address Nigeria’s persistent energy shortages and bolster the country’s energy security. Looking ahead, energy efficiency should not be seen merely as a cost-saving measure. It must be embraced as a strategic approach for Nigeria’s sustainable development objectives. The future
